
Cybersecurity in the Age of GenAI: Coping with the Exponential Web of Change
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, businesses face a paradoxical challenge: while digital transformation fuels revenue growth, it also exposes them to escalating cyber threats.On the one hand, more than half of the global GDP is driven by digitally transformed organizations by now (IDC, 2020). On the other hand, this digital revolution, while fostering economic growth and innovation, also ushers in an era of unprecedented cybersecurity risks. Cybercrime damages are expected to reach a staggering $10.5 trillion annually by 2025 roughly 10% of the projected global GDP, with a concerning annual growth rate of 15%. The complexity and scale of these threats highlight the inadequacy of traditional cybersecurity approaches and the urgent need for a paradigm shift.
As we embrace the power of Generative AI to transform most aspects of society, its exponential growth and capabilities bring about new risks and challenges:
Current Risks & Challenges
- No content attribution to GenAI is possible: The origin and authorship of AI-generated content can be difficult or impossible to trace, leading to potential intellectual property and copyright issues.
- Realistic Content Fabrication without the possibility to prove otherwise: AI can create highly convincing fake content, including images, videos, and audio, making it challenging to distinguish between real and fabricated information.
- Decision-making is more and more informed by, and delegated to GenAI: As AI systems become more sophisticated, there’s a growing reliance on them for decision-making, raising concerns about accountability, transparency, and potential biases.
- Sophisticated Social Engineering through personalized Deep Fakes: AI-powered deepfakes can be used to create highly personalized and deceptive content, increasing the risk of social engineering attacks and targeted scams.
- AI Malware Development at Scale: AI can be used to automate and accelerate the development of malicious software, making it more challenging for traditional cybersecurity defenses to keep up.
These risks and challenges, combined with the rapid pace of AI development, create a heightened threat environment that demands robust and adaptable cybersecurity defenses.
To navigate this complex landscape, a new approach is needed: Multiparty Zero Trust under Zero Knowledge (MZTZK). This innovative framework combines Self Sovereign Identity, Verifiable Execution, and Smart Contracts to establish a decentralized network where every participant is authenticated, every transaction is verified, and sensitive data exchange is minimized. By leveraging these technologies, businesses can fortify their digital infrastructure and confidently embrace the transformative potential of Generative AI.
Understanding MZTZK
At its core, MZTZK is about eliminating inherent trust assumptions in digital interactions.
Firstly, instead of relying on perimeter-based defenses or trusting entities based on their network location or their identity status, MZTZK mandates that all transaction counterparties are authenticated and authorized for every transaction. This approach significantly reduces the attack surface and mitigates the risk of unauthorized access.
Secondly, MZTZK emphasizes the verification of the authenticity, integrity, and correctness of every digital transaction and its associated data supply chain. This ensures that data has not been tampered with, and was derived in a verifiably correct manner at every step of the supply chain..
Finally, MZTZK aims to minimize the exchange of sensitive data, ideally reducing it to zero. This is achieved through cryptographic techniques such as zero-knowledge proofs that allow computations to be performed on obfuscated data without revealing the underlying information.
The Baseline Protocol open-source project was conceived as a solution pattern and a standard for MZTZK. It is part of the Ethereum Open Community Projects initiative within the Open Projects program of the Internet standards organization OASIS. The Baseline Protocol has inspired other standards and implementations such as the Metro Ethernet Forums 114 standard (telecommunications industry) and Polygon Nightfall (an enterprise Ethereum Layer 2 scaling solution).
Key Technologies Enabling MZTZK
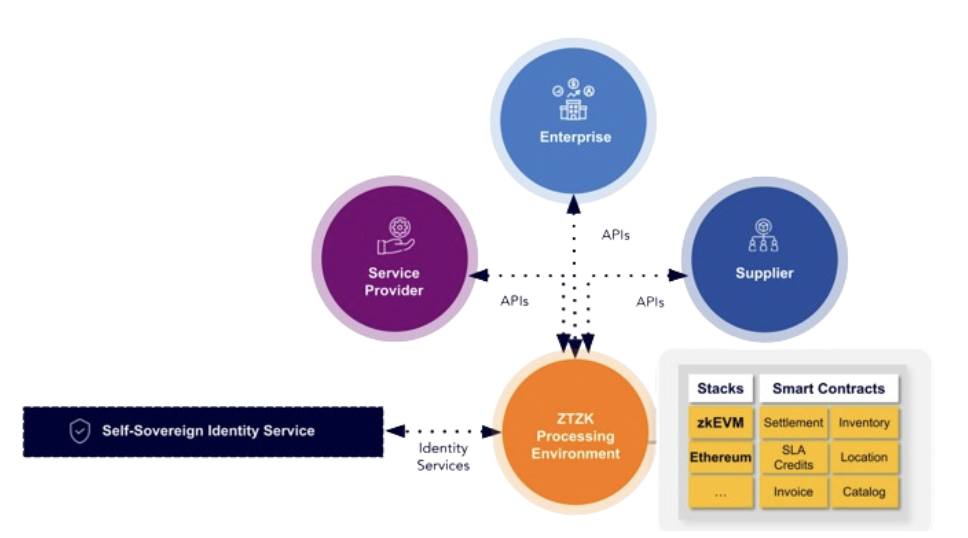
MZTZK leverages several key technologies to achieve its objectives:
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI): SSI provides individuals and organizations with control over their digital identities. It eliminates single points of failure, ensures non-repudiation, and uses established standards for secure and verifiable digital identities. SSI can also be applied to GenAI content and models, addressing the attribution problem.
Verifiably Correct Execution Environments: This technology allows for verifiable cryptographic correctness of digital transactions and their data supply chain. It ensures that computations are performed correctly and that the results can be trusted. An example of such an environment is a zkEVM, a smart contract execution environment that can provide privacy and verifiable correctness for smart contract execution through zero-knowledge proofs. It simplifies the use of smart contracts and generates privacy-preserving proof of correct execution. When these zero-knowledge proofs are anchored and verified on public blockchain networks, in particular public Ethereum, these execution environments inherit the same security guarantees as the underlying public blockchain A significant security improvement when dealing with business processes between essentially untrusted parties as is the case in any supply chain with more than just one buyer and one seller.
Smart Contracts: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automate complex processes and reduce the need for intermediaries, enhancing efficiency and transparency.
Privacy in Smart Contracts
Privacy is a paramount concern in the age of digital transactions and AI-driven surveillance. MZTZK addresses this through a multi-layered approach:
Private Trusted Identity: W3C Decentralized Identifiers anchored on a Blockchain and W3C Verifiable Credentials from trusted issuers ensure that smart contract identities are verifiable without revealing sensitive information to third parties.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs of Correct Execution: Zero-knowledge proofs enable the verification of smart contract execution without disclosing the underlying data in a verifiably correct execution environment such as a zkEVM. This ensures that the privacy of sensitive information is preserved while maintaining the integrity of the transaction and its results.
Zero-Knowledge Proofs within Smart Contracts: Zero-knowledge proofs can also be used within smart contracts to protect the privacy of sensitive data used in business logic execution.
This means that the combination of these technologies can prevent genAI models from learning anything about business process patterns between companies by simply observing data exchanges between companies and correlating them to public news information, as well as leading company data available on the Dark Web.
The Future of Cybersecurity
In summary, the convergence of digital transformation and Generative AI necessitates a robust, adaptable, and privacy-preserving cybersecurity framework. MZTZK offers a promising solution by combining decentralized networks, continuous authentication, verifiable transactions, and minimal data exchange. This approach is critical for future business success as it provides
Enhanced Trust through SSI, Smart Contracts, and private verifiable execution environments
Better Privacy through privacy-preserving proofs in the verifiable execution environments & SSI
Enhanced Security through public Ethereum security guarantees & advanced cryptography (privacy-preserving)
Process Automation through (standardized) Smart Contracts
No Single Point of Failure by combining SSI, verifiably correct execution environments, and public Ethereum
As organizations continue to embrace digital technologies and AI, MZTZK will play a crucial role in safeguarding sensitive data, ensuring the integrity of digital transactions, and fostering trust in an increasingly interconnected world. By adopting MZTZK, businesses can protect themselves against evolving cyber threats and unlock new opportunities for innovation, growth, and collaboration in the digital economy.
It is time, come join us!
Email us at baseline-team@oasis-open.org to join the community.